Introduction
Organic farming in India has witnessed a significant surge in popularity over recent years. Emphasizing sustainability and natural processes, this method is increasingly adopted by farmers and embraced by consumers alike. However, the rise of organic food in India presents a unique blend of benefits and challenges, requiring a deep dive into its multifaceted landscape to understand its impact fully.
Historical Context of Organic Farming in India
Early Agricultural Practices
India’s agricultural history is deeply rooted in traditional organic farming methods. For centuries, Indian farmers relied on natural fertilizers, crop rotation, and indigenous practices to cultivate their crops. These methods were inherently sustainable, maintaining soil health and biodiversity while providing nutritious food.
Transition to Conventional Farming
The Green Revolution in the mid-20th century marked a significant shift towards conventional farming. The introduction of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and high-yield variety seeds transformed Indian agriculture, dramatically increasing productivity. However, this transition also led to environmental degradation, soil depletion, and health concerns, setting the stage for a renewed interest in organic methods.
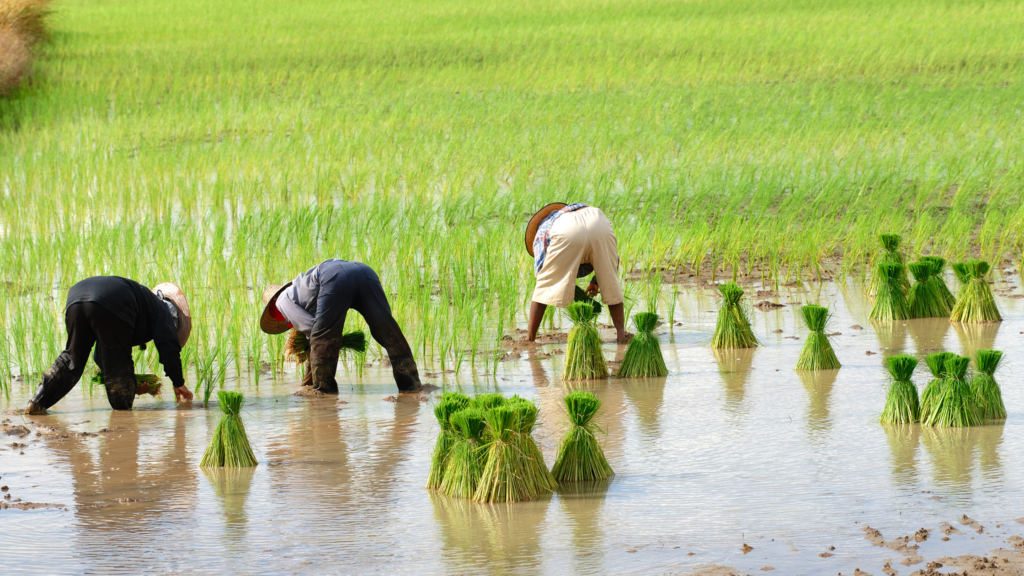

The Emergence of Organic Farming
Pioneers of Organic Movement in India
In the late 20th century, a handful of visionary farmers began advocating for a return to organic methods, emphasizing the need for sustainability and health. These pioneers, including prominent figures like Vandana Shiva, laid the foundation for the organic farming movement in India, demonstrating its viability and benefits through their practices.
Government Initiatives and Policies
Recognizing the potential benefits of organic farming, the Indian government introduced various policies and programs to support it. Initiatives like the Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY) and the National Program for Organic Production (NPOP) provide subsidies, training, and certification processes, aiming to make organic farming more accessible and sustainable for farmers.
Current Trends in Organic Farming
Market Growth and Consumer Demand
The organic food market in India is growing at an impressive rate, driven by increasing health consciousness and environmental awareness among consumers. Organic products, once confined to niche markets, are now available in mainstream supermarkets and online platforms, reflecting the rising consumer demand.
Regional Variations in Adoption
Adoption rates of organic farming vary across regions, with states like Sikkim achieving the status of fully organic, while others are still in the nascent stages. States such as Kerala, Uttarakhand, and Mizoram are also making significant strides, supported by state-specific policies and the unique agro-ecological conditions that favor organic farming.
Benefits of Organic Farming
Health Benefits for Consumers
Organic food is often touted for its superior nutritional content and the absence of harmful chemicals. Studies suggest that organic produce contains higher levels of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, making it a healthier choice for consumers. Moreover, the absence of synthetic pesticides reduces the risk of health issues related to chemical exposure.
Environmental Advantages
Organic farming practices enhance soil fertility, reduce pollution, and promote biodiversity, making them more sustainable than conventional methods. Techniques like composting, crop rotation, and the use of natural pest control methods help maintain ecological balance and prevent soil degradation.
Socio-Economic Impact on Farmers
Organic farming can empower small farmers by reducing dependence on costly chemical inputs and enhancing the economic viability of their farms. By adopting organic methods, farmers can achieve higher profit margins due to premium pricing of organic produce, coupled with reduced input costs.
Challenges Facing Organic Farming
Certification and Regulatory Hurdles
Obtaining organic certification in India is a complex and often costly process, posing a significant barrier for many farmers. The rigorous standards and frequent inspections required for certification can be daunting, particularly for small-scale farmers who lack the necessary resources and support.
Higher Costs and Lower Yields
Organic farming can result in higher production costs and initially lower yields compared to conventional farming, making it economically challenging. The transition period from conventional to organic farming can be particularly tough, as farmers adjust to new practices and face potential income losses.
Limited Awareness and Education
Many farmers lack the knowledge and training needed to transition to and sustain organic farming practices. Limited access to information and education on organic methods can hinder the widespread adoption of organic farming, emphasizing the need for comprehensive training programs and awareness campaigns.
Health Benefits of Organic Food
Nutritional Superiority
Studies suggest that organic food may contain higher levels of certain nutrients, such as antioxidants, compared to conventionally grown produce. This nutritional superiority is attributed to the absence of synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, allowing plants to produce more natural compounds that contribute to human health.
Reduced Exposure to Pesticides
Organic farming eliminates the use of synthetic pesticides, reducing the risk of pesticide exposure for consumers. This reduction is particularly important in India, where pesticide overuse in conventional farming has led to numerous health issues, including chronic illnesses and developmental problems in children.
Environmental Benefits
Soil Health and Fertility
Organic farming practices, such as crop rotation and the use of compost, significantly improve soil health and fertility over time. These methods enhance soil structure, increase organic matter content, and promote beneficial microbial activity, leading to more resilient and productive agricultural systems.
Biodiversity Preservation
Organic farms support greater biodiversity, providing habitats for various species and maintaining ecological balance. The use of diverse crop rotations and natural pest control methods helps sustain a wide range of plant and animal life, contributing to the overall health of the ecosystem.
Socio-Economic Impact
Empowerment of Small Farmers
Organic farming can empower small farmers by promoting self-reliance and reducing input costs. By focusing on locally available resources and traditional knowledge, organic farming enables smallholders to break free from the cycle of debt often associated with chemical inputs and genetically modified seeds.
Rural Development
The rise of organic farming can contribute to rural development by creating new market opportunities and jobs. The growth of the organic sector stimulates local economies, encouraging investment in infrastructure, processing facilities, and marketing channels that benefit rural communities.
Government Policies and Support
Subsidies and Incentives
The Indian government offers various subsidies and incentives to promote organic farming, making it more accessible to farmers. These include financial assistance for certification, support for organic input production, and subsidies for adopting organic practices, all aimed at reducing the economic barriers to entry.
National Programs and Campaigns
Programs like the Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY) and the Mission Organic Value Chain Development for North Eastern Region (MOVCDNER) aim to encourage traditional farming practices and support organic farming. These initiatives provide comprehensive support, including training, certification, and market linkage, to facilitate the growth of organic farming.
Market Dynamics
Consumer Trends and Preferences
A growing segment of Indian consumers prefers organic food due to health and environmental concerns, driving market demand. This trend is reflected in the increasing availability of organic products in supermarkets, specialty stores, and online platforms, catering to the evolving preferences of health-conscious consumers.
Retail and Distribution Networks
The distribution network for organic food is expanding, with more retailers and online platforms offering organic products. This growth is supported by improved logistics, dedicated organic sections in supermarkets, and the proliferation of farmers’ markets and organic food fairs that connect consumers directly with producers.
Certification Process
National and International Standards
Organic certification in India is governed by standards set by organizations such as the National Program for Organic Production (NPOP) and equivalency arrangements with international standards. These standards ensure that organic products meet specific criteria related to production, processing, and labeling, maintaining consumer trust.
Challenges in Obtaining Certification
The certification process is rigorous and expensive, often deterring small farmers from seeking certification. The costs associated with certification, along with the administrative burden of compliance, can be prohibitive, highlighting the need for more accessible and streamlined certification processes.

Case Studies of Successful Organic Farms
Examples from Different Regions
Successful organic farms across India showcase diverse practices and strategies that have led to their success. For instance, Navdanya in Uttarakhand, an initiative by Vandana Shiva, promotes biodiversity and sustainable agriculture, while farms in Sikkim demonstrate the feasibility of state-wide organic farming.
Best Practices and Innovations
Innovations in organic farming, such as integrated pest management and the use of biopesticides, are being adopted by many successful farmers. These practices enhance productivity and sustainability, offering valuable lessons for other farmers looking to transition to organic methods.
Role of Technology in Organic Farming
Modern Techniques and Tools
Technological advancements, such as precision farming and organic farming apps, are aiding farmers in improving productivity and sustainability. Tools like drones for monitoring crop health and soil sensors for optimizing water use are becoming increasingly accessible to organic farmers.
Digital Platforms and Marketplaces
Online marketplaces and digital platforms are helping farmers sell their organic produce directly to consumers, enhancing market reach. Platforms like KisanMandi and Farmizen facilitate direct sales, reducing intermediaries and ensuring better prices for farmers.

Educational and Awareness Programs
Training for Farmers
Numerous training programs and workshops are being conducted to educate farmers about organic farming practices. These programs, often organized by government agencies, NGOs, and private entities, provide hands-on training and technical support to help farmers adopt and sustain organic methods.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns aim to inform consumers about the benefits of organic food, driving demand and supporting farmers. Initiatives like the Organic Food Festival and media campaigns highlight the health and environmental advantages of organic produce, encouraging more people to make the switch.
International Influence and Collaboration
Learning from Global Practices
Indian organic farming is benefiting from global knowledge exchange and best practices, enhancing local farming techniques. Collaboration with international organizations and participation in global forums provide Indian farmers with exposure to advanced organic farming practices and innovations.
Export Opportunities and Challenges
While there is significant export potential for Indian organic products, challenges such as stringent international standards and market access barriers remain. Overcoming these challenges requires robust certification processes, quality assurance, and effective marketing strategies to tap into global markets.
The Future of Organic Farming in India
Predictions and Projections
Experts predict continued growth in the organic farming sector, driven by increasing consumer demand and government support. The sector is expected to expand as more farmers adopt organic methods and as new policies and technologies make organic farming more viable and profitable.
Emerging Trends and Innovations
Innovations such as vertical farming and urban organic gardens are expected to shape the future of organic farming in India. These trends, along with the growing emphasis on sustainability and climate resilience, point towards a dynamic and evolving organic farming landscape.
Consumer Perspective
Why Consumers Choose Organic
Consumers are increasingly choosing organic food for its perceived health benefits and environmental impact. The preference for organic products is driven by concerns about food safety, nutrition, and sustainability, with many consumers willing to pay a premium for these perceived advantages.
Perceived Benefits vs. Actual Benefits
While many consumers believe in the superiority of organic food, it is important to balance perceptions with scientific evidence. Ongoing research and transparent communication are crucial to addressing misconceptions and providing consumers with accurate information about the benefits of organic food.
Criticisms and Controversies
Debates on Efficacy and Sustainability
There are ongoing debates about the efficacy and long-term sustainability of organic farming compared to conventional methods. Critics argue that organic farming cannot meet the food demands of a growing population, while proponents emphasize its environmental and health benefits.
Addressing Skepticism
Addressing consumer skepticism through education and transparent practices is crucial for the continued growth of the organic sector. Clear labeling, rigorous certification, and public education campaigns can help build trust and confidence in organic products.
Conclusion
Summarizing Benefits and Challenges
Organic farming in India offers numerous benefits, including improved health, environmental sustainability, and socio-economic empowerment. However, it also faces significant challenges, such as certification hurdles, higher costs, and limited awareness, which need to be addressed collectively.
Call to Action for Stakeholders
A concerted effort by farmers, consumers, policymakers, and industry stakeholders is essential to realize the full potential of organic farming in India. By working together, we can create a sustainable and healthy agricultural future that benefits everyone.
For organic food product click here
For more content follow Humstory