Introduction
Karnataka is on the cusp of a significant environmental milestone as it prepares to launch trials for its first waste-to-energy plant in Bidadi. This innovative project aims to manage waste more effectively while generating energy, addressing two critical issues simultaneously. Waste to energy technology represents a promising solution for sustainable waste management and energy production.
Background of the Project
The journey of Karnataka’s first waste-to-energy plant began several years ago, driven by the growing need for effective waste management solutions. The planning phase involved extensive research and collaboration between various stakeholders, including government bodies, environmental organizations, and private investors. The project received substantial funding, showcasing a strong commitment to tackling waste and energy challenges innovatively. The concept of waste to energy was not new, but implementing it on this scale in Karnataka required careful consideration of various factors, including technological feasibility, environmental impact, and economic viability.
Location and Significance of Bidadi
Bidadi, strategically located near Bengaluru, was selected for its geographical and infrastructural advantages. The proximity to the city ensures a steady supply of waste, while the available land and resources make it an ideal site for such a project. Bidadi’s selection underscores the importance of choosing locations that offer logistical benefits for large-scale environmental projects. Additionally, the choice of Bidadi highlights the region’s commitment to becoming a hub for innovative waste management solutions, setting a precedent for other areas to follow suit.
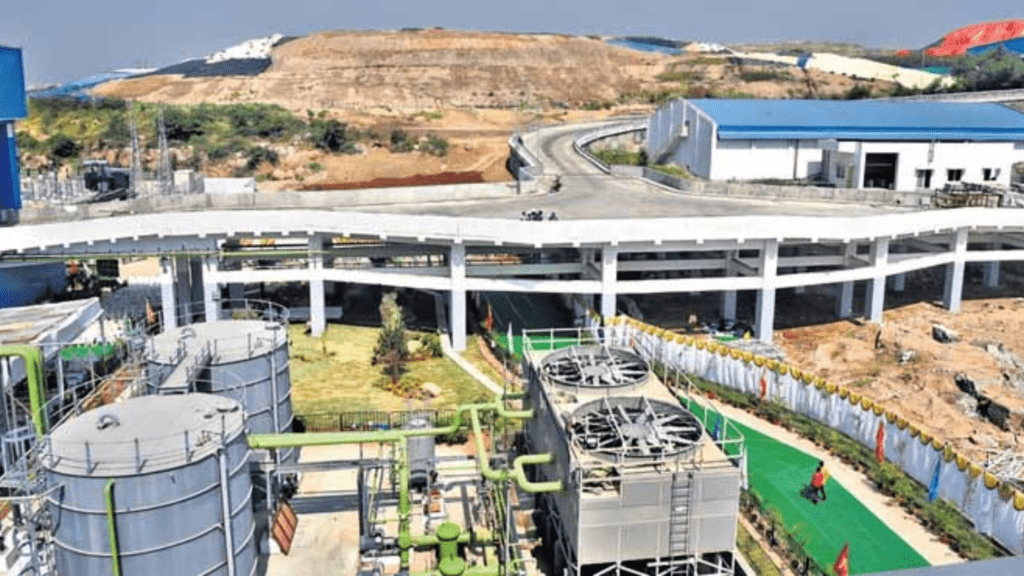

Technology Behind Waste-to-Energy
At the heart of the Bidadi plant is cutting-edge waste-to-energy technology. This process involves converting municipal solid waste into energy through various methods such as incineration, gasification, and anaerobic digestion. The Bidadi plant will primarily use incineration, where waste is burned at high temperatures to produce steam that drives turbines, generating electricity. This technology not only reduces the volume of waste but also produces a reliable source of renewable energy. The efficiency and environmental benefits of waste to energy make it an attractive option for sustainable waste management.
Environmental Impact
The environmental benefits of waste-to-energy technology are manifold. Firstly, it significantly reduces the amount of waste that ends up in landfills, thus mitigating the associated environmental hazards. Landfills are known to produce methane, a potent greenhouse gas, contributing to climate change. By diverting waste from landfills to the waste to energy plant, Karnataka is making a positive impact on reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Moreover, the energy produced from waste is renewable, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. Compared to traditional waste disposal methods, waste to energy offers a more sustainable and eco-friendly solution. This technology also helps in recovering valuable metals and other materials from waste, promoting a circular economy.
Economic Implications
The Bidadi waste-to-energy project represents a substantial financial investment, with costs running into hundreds of crores. However, the long-term economic benefits far outweigh the initial expenditure. By generating electricity from waste, the plant will provide a steady revenue stream, reduce energy costs, and create numerous jobs. Additionally, the project is expected to attract further investments in sustainable technologies, boosting Karnataka’s economy. The waste to energy sector also has the potential to spur innovation and development in related industries, further enhancing economic growth.
Challenges and Concerns
Despite its potential, the project faces several challenges. Technically, the integration of waste-to-energy technology into existing waste management systems is complex and requires meticulous planning. Ensuring a consistent and adequate supply of waste, maintaining high efficiency in energy conversion, and managing emissions are some of the technical hurdles. Public concerns also present a hurdle, with some communities expressing apprehension about potential environmental and health impacts. Addressing these concerns through transparent communication and stringent regulatory measures is crucial for the project’s success. Engaging with local communities, providing accurate information, and demonstrating the environmental and economic benefits of waste to energy can help in gaining public support.
Government and Policy Support
The successful implementation of Karnataka’s waste-to-energy plant is heavily reliant on supportive government policies. Both the state and national governments have introduced various incentives and regulations to promote renewable energy projects. These policies include subsidies, tax benefits, and streamlined approval processes, all aimed at fostering a favorable environment for such initiatives. Government support is essential not only in terms of financial incentives but also in providing the necessary infrastructure and regulatory framework to ensure the smooth functioning of the waste to energy plant.
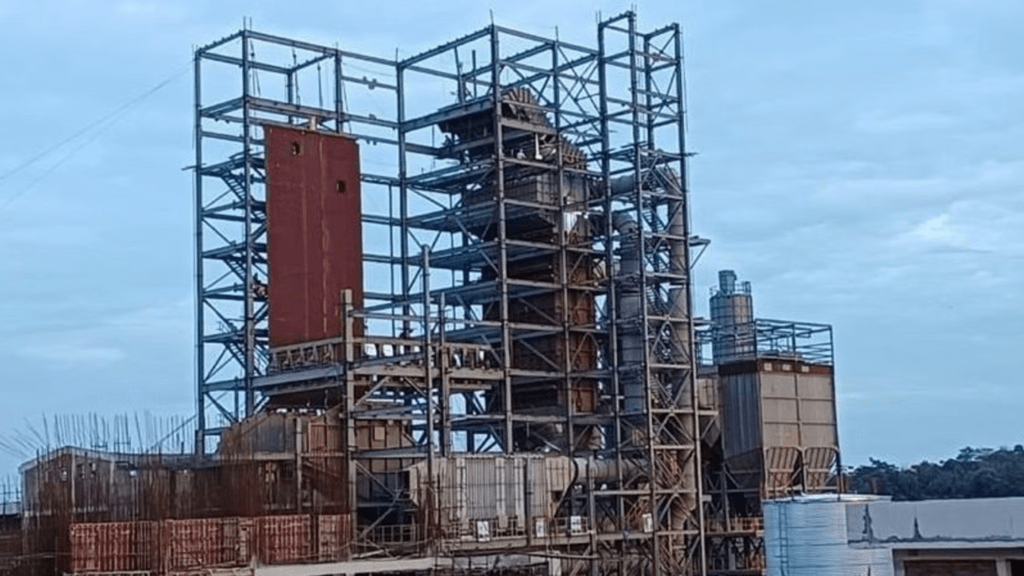
Trial Phase Details
The trial phase of the Bidadi waste-to-energy plant is set to begin by mid-July. This phase will involve rigorous testing of all systems to ensure operational efficiency and safety. Engineers and technicians will monitor the plant’s performance, make necessary adjustments, and validate the technology’s effectiveness. The trial phase is a critical step in ensuring the plant’s readiness for full-scale operation. It will also provide valuable data and insights that can be used to optimize the plant’s performance and address any issues that may arise during the initial stages.
Future Prospects and Expansion
Looking ahead, the Bidadi plant is just the beginning. Karnataka plans to establish additional waste-to-energy plants across the state, leveraging the success and learnings from the Bidadi project. This expansion holds the potential to transform waste management practices, making Karnataka a leader in sustainable energy solutions. Furthermore, the model developed in Karnataka could be replicated in other regions, promoting wider adoption of waste-to-energy technology. The future of waste to energy in Karnataka looks promising, with the potential to significantly reduce waste, generate renewable energy, and create economic opportunities.

Conclusion
Karnataka’s first waste-to-energy plant marks a pivotal moment in the state’s environmental and energy strategy. As the Bidadi plant embarks on its trial phase, it stands as a testament to the innovative spirit and commitment to sustainability. This project not only promises to address waste management challenges but also paves the way for a greener, more energy-efficient future. The successful implementation of waste to energy technology in Karnataka could serve as a blueprint for other regions, demonstrating the feasibility and benefits of such projects on a larger scale. By embracing waste to energy, Karnataka is taking a significant step towards a sustainable future, setting an example for others to follow.
For more content follow Humstory