Introduction
Overview of Chandrayaan-3 Mission
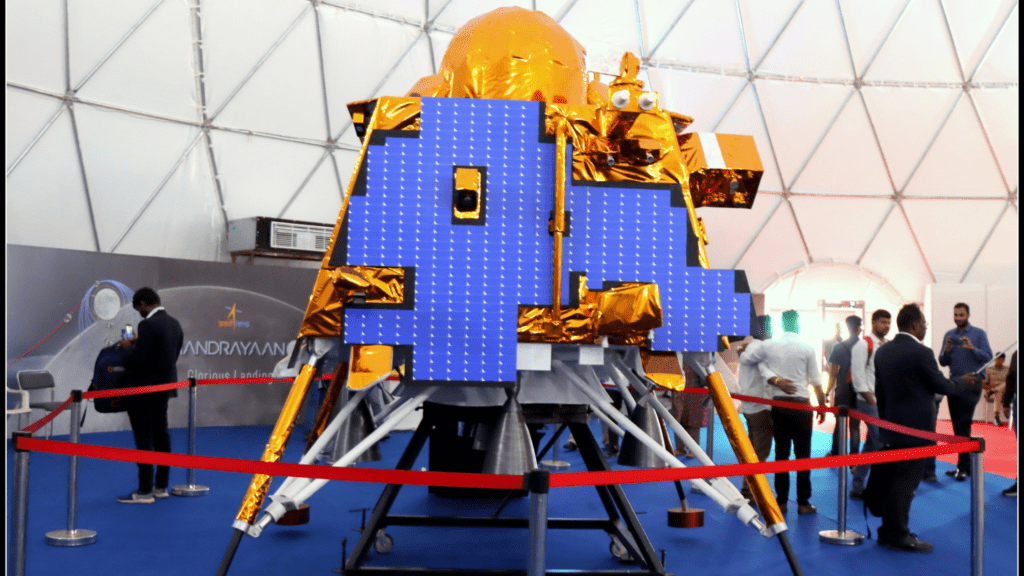
Chandrayaan-3, India’s third lunar exploration mission, stands as a testament to the nation’s advancing space capabilities. Managed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), this mission aimed to further our understanding of the Moon, particularly its enigmatic south pole. This region has intrigued scientists worldwide due to its unique characteristics and potential for new discoveries.
Significance of Moon’s South Pole Exploration
The Moon’s south pole holds scientific allure due to its permanently shadowed craters, which may harbor water ice and other volatile compounds. These resources could be pivotal for future manned missions, providing essential materials for sustaining human presence and facilitating deeper space exploration.
Chandrayaan-3: A Technological Marvel
Key Features of Chandrayaan-3
Chandrayaan-3 showcases cutting-edge technology with its robust design and advanced scientific instruments. Unlike its predecessor, Chandrayaan-2, this mission focuses solely on landing and rover exploration, eliminating the orbiter component to streamline its objectives.
The Pragyan Rover: Design and Capabilities
The Pragyan rover, an integral part of Chandrayaan-3, is engineered for durability and efficiency. Equipped with high-resolution cameras, spectrometers, and a suite of scientific instruments, Pragyan is capable of conducting detailed analyses of the lunar surface, providing unprecedented insights into the Moon’s geology and composition.
The Journey to the Moon
Launch and Trajectory
Chandrayaan-3 embarked on its journey from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, utilizing a powerful launch vehicle to escape Earth’s gravitational pull. The trajectory was meticulously calculated to ensure a precise landing at the Moon’s south pole, a feat requiring immense precision and expertise.
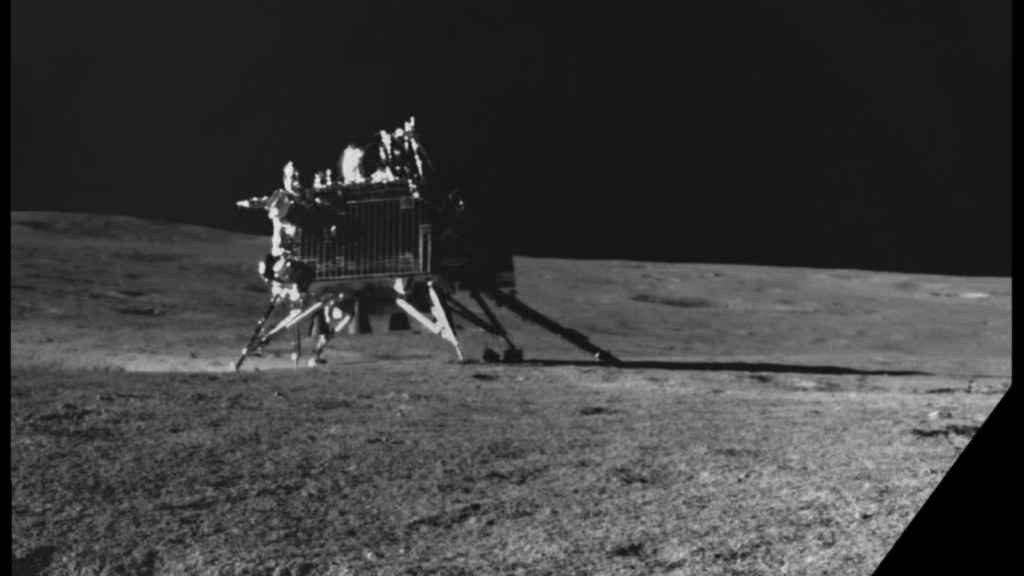
Landing at the South Pole
The landing was a critical phase, executed with remarkable accuracy. Pragyan rover descended gently onto the lunar surface, touching down in a region teeming with scientific potential. This successful landing marked a significant milestone in India’s space exploration history.
Initial Findings
Surface Composition Analysis
Pragyan’s initial analysis of the lunar surface revealed a composition rich in silicates, oxides, and other minerals. These findings provide valuable data for understanding the Moon’s formation and geological evolution.
Presence of Water Ice
One of the mission’s most anticipated discoveries was the detection of water ice in permanently shadowed craters. Using advanced spectrometers, Pragyan confirmed the presence of water molecules, bolstering the theory that the Moon’s poles contain significant ice deposits.
Geological Discoveries
Unique Rock Formations
The south pole’s terrain is marked by distinct rock formations, unlike any found in other lunar regions. Pragyan’s high-resolution imagery captured these formations, offering clues about the Moon’s volcanic past and tectonic activity.
Evidence of Volcanic Activity
Pragyan’s data suggests that the south pole experienced volcanic activity billions of years ago. The presence of basaltic rocks and volcanic glass indicates that this region underwent significant geological processes, contributing to our understanding of lunar volcanism.
Temperature Extremes
Day and Night Temperature Variations
The temperature at the Moon’s south pole varies dramatically between day and night. Pragyan recorded extreme temperatures, ranging from the frigid cold of lunar night to the intense heat of daytime. These variations pose challenges for future exploration and habitation.
Implications for Future Missions
Understanding these temperature extremes is crucial for designing equipment and habitats for future missions. Chandrayaan-3’s data will aid in developing technologies that can withstand the harsh lunar environment, ensuring the safety and success of future explorers.
Mineralogical Insights
Detection of Rare Minerals
Pragyan’s spectrometers detected a range of rare minerals, including some not commonly found on Earth. These findings could provide insights into the Moon’s formation and the processes that shaped its surface.
Comparison with Earth’s Minerals
The mineralogical data collected by Pragyan allows for direct comparison with Earth’s geology. Understanding these similarities and differences can enhance our knowledge of planetary formation and the dynamic processes that govern celestial bodies.
Lunar Dust Analysis
Composition of Lunar Regolith
Lunar regolith, the layer of loose, fragmented material covering solid rock, was analyzed in detail by Pragyan. The composition includes fine dust and larger particles, offering clues about the Moon’s surface processes and the effects of space weathering.
Challenges for Equipment and Future Exploration
Lunar dust presents significant challenges for equipment due to its abrasive nature. Chandrayaan-3’s findings will inform the design of future missions, helping to mitigate the impact of lunar dust on machinery and instrumentation.
Radiation Levels
Measuring Radiation at the South Pole
Pragyan’s instruments measured radiation levels at the south pole, providing critical data for assessing the safety of future manned missions. The Moon’s lack of atmosphere exposes its surface to high levels of cosmic radiation, posing risks to both equipment and human health.
Safety Considerations for Astronauts
Understanding radiation levels is essential for planning long-duration missions. Chandrayaan-3’s data will aid in developing protective measures and habitats to shield astronauts from harmful radiation, ensuring their well-being during lunar expeditions.
Magnetic Field Observations
Localized Magnetic Anomalies
Pragyan detected localized magnetic anomalies at the Moon’s south pole, suggesting the presence of ancient magnetic fields. These anomalies provide insights into the Moon’s geological history and the processes that shaped its magnetic environment.
Impact on Navigation and Communication
Magnetic anomalies can affect navigation and communication systems. Chandrayaan-3’s findings will help in designing robust technologies that can operate effectively in the Moon’s complex magnetic environment, ensuring reliable communication for future missions.
The Search for Organic Compounds
Techniques Used
Pragyan employed advanced techniques to search for organic compounds, including spectroscopy and chromatography. These methods are sensitive enough to detect trace amounts of organic materials, offering a glimpse into the Moon’s potential to harbor life.
Potential for Past Life Indicators
While the primary focus was on inorganic materials, the detection of organic compounds could indicate past life or prebiotic chemistry. Chandrayaan-3’s search contributes to the broader quest to understand the origins of life in our solar system.
Pragyan Rover’s Mobility and Longevity
Distance Covered and Terrain Challenges
Pragyan traversed a considerable distance, navigating the rugged terrain of the south pole. The rover’s mobility and ability to overcome obstacles highlight its engineering prowess and the careful planning behind its mission.
Battery Life and Energy Efficiency
Pragyan’s energy efficiency and battery life were critical for the mission’s success. The rover utilized solar panels to recharge its batteries, ensuring continuous operation and data collection even in the harsh lunar environment.

Scientific Experiments Conducted
Key Experiments and Their Outcomes
Pragyan conducted a series of scientific experiments, including soil analysis, mineral detection, and radiation measurement. These experiments yielded valuable data, enhancing our understanding of the Moon’s south pole and its potential for future exploration.
Collaboration with International Space Agencies
Chandrayaan-3’s mission was a collaborative effort involving international space agencies. This cooperation facilitated the exchange of knowledge and resources, advancing the global scientific community’s understanding of lunar science.
Implications for Human Exploration
Preparing for Manned Missions
The findings from Chandrayaan-3 will inform the planning of future manned missions to the Moon. Understanding the south pole’s environment is crucial for developing sustainable habitats and ensuring the safety of astronauts.
Utilization of Lunar Resources
The detection of water ice and other resources at the south pole opens the possibility of utilizing these materials for life support and fuel. Chandrayaan-3’s discoveries pave the way for in-situ resource utilization, a key component of long-term lunar exploration.
Future of Lunar Exploration
Upcoming Missions and Technologies
Chandrayaan-3’s success sets the stage for future lunar missions, both by ISRO and other space agencies. Upcoming missions will build on its findings, employing advanced technologies to explore the Moon’s surface and subsurface in greater detail.
Chandrayaan-3’s Legacy
Chandrayaan-3 has cemented its legacy as a groundbreaking mission that advanced our understanding of the Moon’s south pole. Its discoveries will continue to influence lunar science and exploration, inspiring future generations of scientists and engineers.
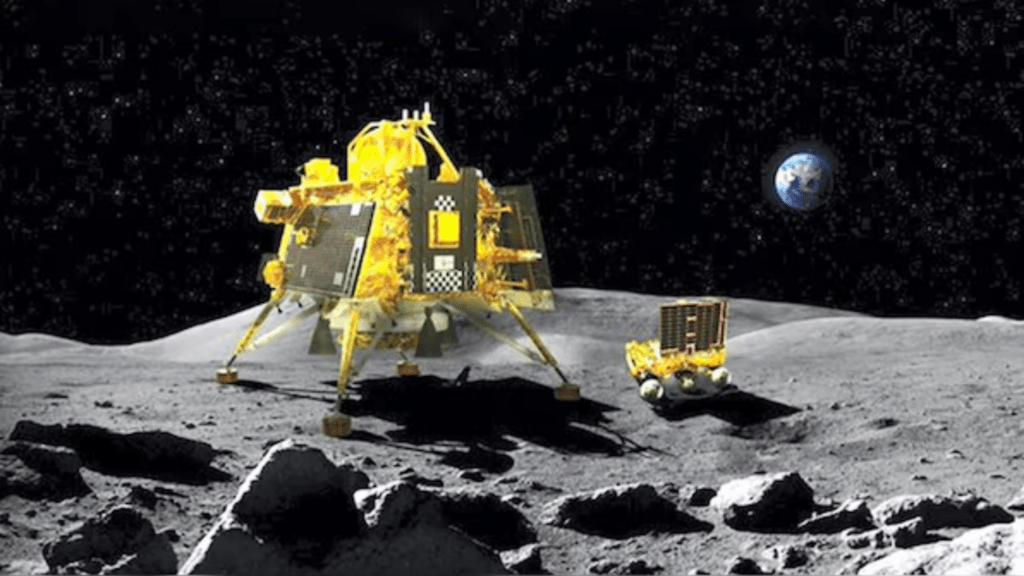
Chandrayaan-3’s Pragyan rover has provided invaluable insights into the Moon’s south pole, uncovering new findings that enhance our understanding of this enigmatic region. From detecting water ice to analyzing unique geological formations, Pragyan’s discoveries hold significant implications for future lunar missions and the broader field of planetary science. As we continue to explore the Moon and beyond, Chandrayaan-3’s legacy will undoubtedly inspire and inform the next wave of space exploration.
References
- Times of India. Chandrayaan-3’s Pragyan Rover Makes New Findings at Moon’s South Pole. Retrieved from https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/chandrayaan-3s-pragyan-rover-makes-new-findings-at-moons-south-pole/articleshow/111441287.cms
- Business Standard. Chandrayaan-3’s Rover Makes Significant Discoveries on Moon’s South Pole. Retrieved from https://www.business-standard.com/india-news/chandrayaan-s-rover-makes-significant-discoveries-on-moon-s-south-pole-124070200814_1.html
For more content follow Humstory